Markdown Converter
Agent skill for markdown-converter
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
Sign in to like and favorite skills
<!--[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]opyright 2024 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eam. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ll rights reserved.
Licensed under the [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]pache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/L[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]-2.0
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
an "[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S" [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S, W[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] W[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]D[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]D, either express or implied. See the License for the
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
⚠️ [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ote that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
--[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]
# 智能体和工具
[[在colab里打开]]
### 什么是智能体 ([YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent)?
大型语言模型(LLM)经过 [因果语言建模训练](./tasks/language[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]modeling) 可以应对各种任务,但在一些基本任务(如逻辑推理、计算和搜索)上常常表现不佳。当它们被用在自己不擅长的领域时,往往无法生成我们期望的答案。
为了解决这个问题,可以创建**智能体**.
智能体是一个系统,它使用 LLM 作为引擎,并且能够访问称为**工具**的功能。
这些**工具**是执行任务的函数,包含所有必要的描述信息,帮助智能体正确使用它们。
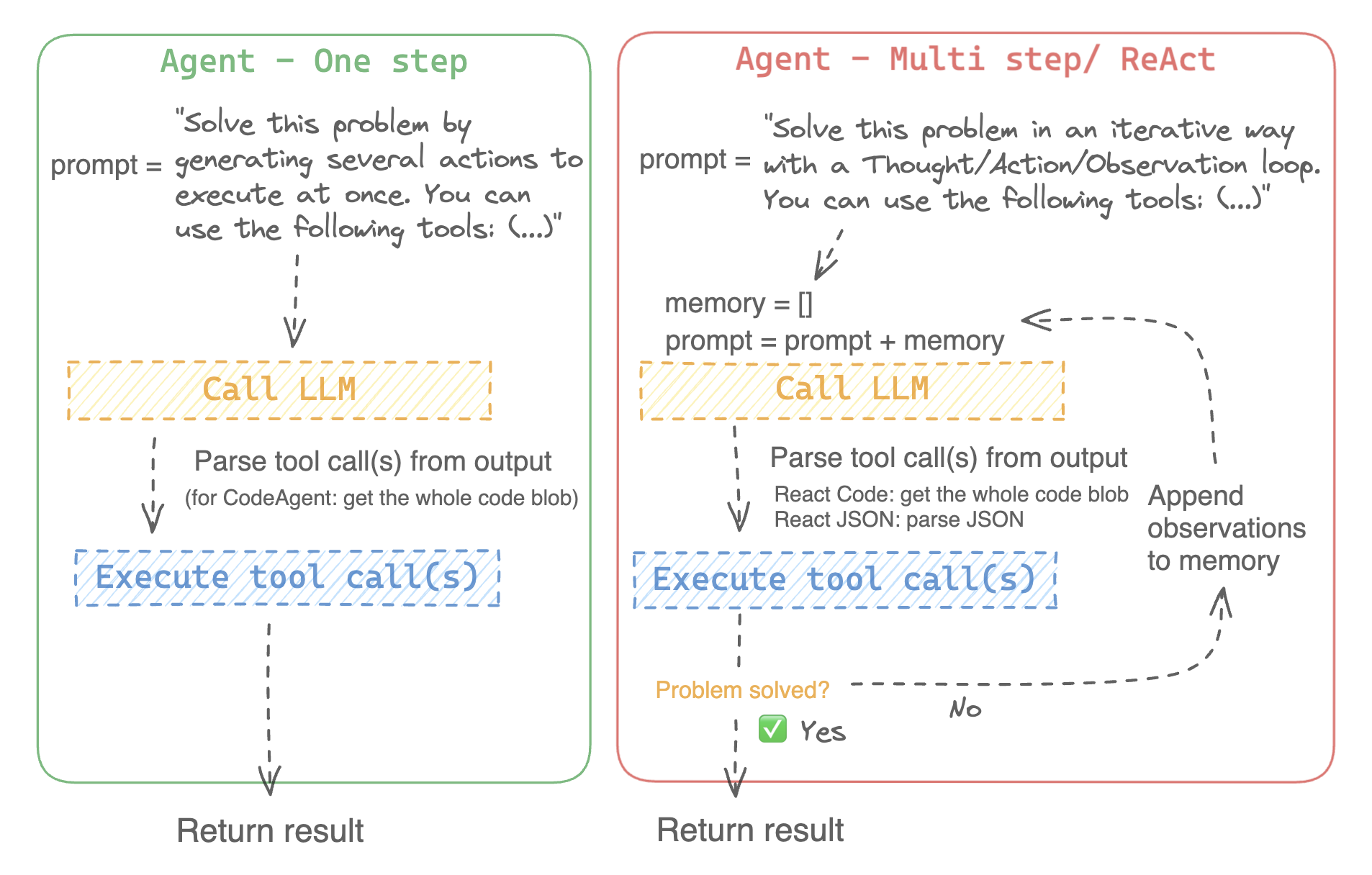
智能体可以被编程为:
- 一次性设计一系列工具并同时执行它们,像 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`]
- 一次执行一个工具,并等待每个工具的结果后再启动下一个,像 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eactJson[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`]
### 智能体类型
#### 代码智能体
此智能体包含一个规划步骤,然后生成 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython 代码一次性执行所有任务。它原生支持处理不同输入和输出类型,因此推荐用于多模态任务。
#### 推理智能体
这是解决推理任务的首选代理,因为 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]e[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ct 框架 ([[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ao et al., 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) 使其在基于之前观察进行推理时非常高效。
我们实现了两种版本的 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eactJson[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent:
- [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eactJson[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`] 将工具调用作为 JS[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] 格式输出。
- [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`] 是 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eactJson[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent 的一种新型,生成工具调用的代码块,对于具备强大编程能力的 LLM 非常适用。
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]]
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] 阅读 [[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]pen-source LLMs as Lang[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hain [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) 博文,了解更多关于推理智能体的信息。
<div class="flex justify-center"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]
<img
class="block dark:hidden"
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]Manim[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>].gif"
/[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]
<img
class="hidden dark:block"
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]Manim[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>].gif"
/[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]
</div[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]

以下是一个推理代码智能体如何处理以下问题的示例:
```py3
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] agent.run(
... "[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ow many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ttention is [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ll [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eed?",
... )
=====[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ew task=====
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ow many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ttention is [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ll [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eed?
====[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent is executing the code below:
bert[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]blocks = search(query="number of blocks in [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] base encoder")
print("[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] blocks:", bert[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]blocks)
====
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rint outputs:
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] blocks: twelve encoder blocks
====[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent is executing the code below:
attention[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]layer = search(query="number of layers in [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ttention is [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ll [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eed")
print("[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ttention layers:", attention[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]layer)
====
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rint outputs:
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ttention layers: [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ncoder: [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he encoder is composed of a stack of [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] = 6 identical layers. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ach layer has two sub-layers. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position- 2 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]age 3 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]igure 1: [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ransformer - model architecture.
====[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent is executing the code below:
bert[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]blocks = 12
attention[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]layers = 6
diff = bert[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]blocks - attention[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]layers
print("Difference in blocks:", diff)
final[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]answer(diff)
====
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rint outputs:
Difference in blocks: 6
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]inal answer: 6
```
### 如何构建智能体?
要初始化一个智能体,您需要以下参数:
- **一个 LLM** 来驱动智能体——智能体本身并不是 LLM,而是一个使用 LLM 作为引擎的程序。
- **一个系统提示**:告诉 LLM 引擎应该如何生成输出。
- **一个工具箱**,智能体可以从中选择工具执行。
- **一个解析器**,从 LLM 输出中提取出哪些工具需要调用,以及使用哪些参数。
在智能体系统初始化时,工具属性将生成工具描述,并嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,告知智能体可以使用哪些工具,并且为什么使用它们。
**安装依赖**
首先,您需要安装**智能体**所需的额外依赖:
```bash
pip install transformers[agents]
```
**创建LLM引擎**
定义一个 `llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine` 方法,该方法接受一系列[消息](./chat[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]templating)并返回文本。该 `callable` 还需要接受一个 `stop` 参数,用于指示何时停止生成输出。
```python
from huggingface[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hub import login, [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nference[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]lient
login("<[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]")
client = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nference[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]lient(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]-[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nstruct")
def llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine(messages, stop[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]sequences=["[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ask"]) -[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] str:
response = client.chat[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]completion(messages, stop=stop[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]sequences, max[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tokens=1000)
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
return answer
```
您可以使用任何符合以下要求的 `llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine` 方法:
1. [输入格式](./chat[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]templating)为 (`List[Dict[str, str]]`),并且返回一个字符串。
2. 它在 `stop[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]sequences` 参数传递的序列处停止生成输出。
此外,`llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine` 还可以接受一个 `grammar` 参数。如果在智能体初始化时指定了 `grammar`,则该参数将传递给 `llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine` 的调用,以允许[受限生成](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/conceptual/guidance),以强制生成格式正确的智能体输出。
您还需要一个 `tools` 参数,它接受一个 `[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ools` 列表 —— 可以是空列表。您也可以通过定义可选参数 `add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue` 来将默认工具箱添加到工具列表中。
现在,您可以创建一个智能体,例如 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`],并运行它。您还可以创建一个 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ransformers[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ngine`],使用 `transformers` 在本地机器上运行预初始化的推理管道。 为了方便起见,由于智能体行为通常需要更强大的模型,例如 `Llama-3.1-70[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]-[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nstruct`,它们目前较难在本地运行,我们还提供了 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]f[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]pi[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ngine`] 类,它在底层初始化了一个 `huggingface[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hub.[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nference[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]lient`。
```python
from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent, [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]f[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]pi[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ngine
llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]f[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]pi[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]-[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nstruct")
agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[], llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine=llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine, add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue)
agent.run(
"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ould you translate this sentence from [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rench, say it out loud and return the audio.",
sentence="[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ù est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
)
```
当你急需某个东西时这将会很有用!
您甚至可以将 `llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine` 参数留空,默认情况下会创建一个 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]f[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]pi[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ngine`]。
```python
from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent
agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[], add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue)
agent.run(
"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ould you translate this sentence from [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rench, say it out loud and give me the audio.",
sentence="[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ù est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
)
```
请注意,我们使用了额外的 `sentence` 参数:您可以将文本作为附加参数传递给模型。
您还可以使用这个来指定本地或远程文件的路径供模型使用:
```py
from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent
agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[], llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine=llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine, add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue)
agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ew [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ork?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
```
系统提示和输出解析器会自动定义,但您可以通过调用智能体的 `system[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]prompt[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]template` 来轻松查看它们。
```python
print(agent.system[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]prompt[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]template)
```
尽可能清楚地解释您要执行的任务非常重要。 每次 [`~[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent.run`] 操作都是独立的,并且由于智能体是由 LLM 驱动的,提示中的细微变化可能会导致完全不同的结果。
您还可以连续运行多个任务,每次都会重新初始化智能体的 `agent.task` 和 `agent.logs` 属性。
#### 代码执行
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython 解释器在一组输入和工具上执行代码。 这应该是安全的,因为只能调用您提供的工具(特别是 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace 的工具)和 print 函数,因此您已经限制了可以执行的操作。
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython 解释器默认不允许导入不在安全列表中的模块,因此大多数明显的攻击问题应该不成问题。 您仍然可以通过在 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`] 或 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`] 初始化时通过 `additional[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]authorized[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]imports` 参数传递一个授权的模块列表来授权额外的导入:
```py
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[], additional[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]authorized[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] agent.run("[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ould you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
(...)
'[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace – [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]log'
```
如果有任何代码尝试执行非法操作,或者生成的代码出现常规 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython 错误,执行将停止。
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [!W[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]]
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] 在使用大语言模型(LLM)生成代码时,生成的代码会被执行,避免导入或使用任何不安全的库或模块。
### 系统提示
智能体,或者说驱动智能体的 LLM,根据系统提示生成输出。系统提示可以定制并根据目标任务进行调整。例如,检查 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`] 的系统提示(以下版本经过简化)。
```text
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou will be given a task to solve as best you can.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou have access to the following tools:
<<tool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]descriptions[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]o solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hought:', '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode:', and '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]bservation:' sequences.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]t each step, in the '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hen in the '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode:' sequence, you should write the code in simple [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he code sequence must end with '/[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nd code' sequence.
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hese print outputs will then be available in the '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]bservation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]n the end you have to return a final answer using the `final[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]answer` tool.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ere are a few examples using notional tools:
---
{examples}
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]bove example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou only have acces to those tools:
<<tool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]names[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]lways provide a '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hought:' and a '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]code[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]' sequence. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou M[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]S[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] provide at least the '[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode:' sequence to move forward.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]emember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ou should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rint results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hen use final[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]answer() to return the final result.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]emember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ow [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]egin!
```
系统提示包括:
- 解释智能体应该如何工作以及工具的**介绍**。
- 所有工具的描述由 `<<tool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]descriptions[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]` 标记在运行时动态替换,这样智能体就知道可以使用哪些工具及其用途。
- 工具的描述来自工具的属性,`name`、`description`、`inputs` 和 `output[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]type`,以及一个简单的 `jinja2` 模板,您可以根据需要进行调整。
- 期望的输出格式。
您可以通过向 `system[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]prompt` 参数传递自定义提示来最大程度地提高灵活性,从而覆盖整个系统提示模板。
```python
from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eactJson[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent
from transformers.agents import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nterpreter[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ool
agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eactJson[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nterpreter[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ool()], system[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]prompt="{your[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]custom[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]prompt}")
```
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [W[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]]
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] 必须在`template`中定义 `<<tool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]descriptions[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]` 这个变量,以便智能体能够正确地识别并使用可用的工具
### 检查智能体的运行
以下是检查运行后发生了什么的一些有用属性:
- `agent.logs` 存储了智能体的详细日志。每一步的所有内容都会存储在一个字典中,然后附加到 `agent.logs`。
- 运行 `agent.write[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]inner[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]memory[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]from[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]logs()` 会从日志中创建智能体的内存,以便 LLM 查看,作为一系列聊天消息。此方法会遍历日志的每个步骤,只保存其感兴趣的消息:例如,它会单独保存系统提示和任务,然后为每个步骤保存 LLM 输出的消息,以及工具调用输出的消息。如果您想要更高层次的查看发生了什么,可以使用此方法 —— 但并不是每个日志都会被此方法转录。
## 工具
工具是智能体使用的基本功能。
例如,您可以检查 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nterpreter[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ool`]:它有一个名称、描述、输入描述、输出类型和 `[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]call[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]` 方法来执行该操作。
当智能体初始化时,工具属性会用来生成工具描述,然后将其嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,这让智能体知道可以使用哪些工具以及为什么使用它们。
### 默认工具箱
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ransformers 提供了一个默认工具箱,用于增强智能体,您可以在初始化时通过 `add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue` 参数将其添加到智能体中:
- **文档问答**:给定一个文档(如图像格式的 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]D[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]),回答关于该文档的问题([Donut](./model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]doc/donut))
- **图像问答**:给定一张图片,回答关于该图像的问题([V[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]L[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]](./model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]doc/vilt))
- **语音转文本**:给定一个人讲述的音频录音,将其转录为文本(Whisper)
- **文本转语音**:将文本转换为语音([Speech[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]5](./model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]doc/speecht5))
- **翻译**:将给定的句子从源语言翻译为目标语言
- **DuckDuck[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]o 搜索**:使用 `DuckDuck[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]o` 浏览器进行网络搜索
- **[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython 代码解释器**:在安全环境中运行 LLM 生成的 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython 代码。只有在初始化 [`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eactJson[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent`] 时将 `add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue` 时,代码智能体才会添加此工具,因为基于代码的智能体已经能够原生执行 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ython 代码
您可以通过调用 [`load[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool`] 函数来手动使用某个工具并执行任务。
```python
from transformers import load[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool
tool = load[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool("text-to-speech")
audio = tool("[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]his is a text to speech tool")
```
### 创建新工具
您可以为 `[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace` 默认工具无法涵盖的用例创建自己的工具。
例如,假设我们要创建一个返回在 `[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ub` 上某个任务中下载次数最多的模型的工具。
您将从以下代码开始:
```python
from huggingface[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]hub import list[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]models
task = "text-classification"
model = next(iter(list[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
print(model.id)
```
这段代码可以很快转换为工具,只需将其包装成一个函数,并添加 `tool` 装饰器:
```py
from transformers import tool
@tool
def model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]download[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool(task: str) -[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] str:
"""
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]his is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ub.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]t returns the name of the checkpoint.
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rgs:
task: [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he task for which
"""
model = next(iter(list[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]models(filter="text-classification", sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
return model.id
```
该函数需要:
- 一个清晰的名称。名称通常描述工具的功能。由于代码返回某个任务中下载次数最多的模型,因此我们将其命名为 `model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]download[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool`。
- 对输入和输出进行类型提示
- 描述,其中包括 "`[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rgs`:" 部分,描述每个参数(这次不需要类型指示,它会从类型提示中获取)。
所有这些将自动嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,因此请尽量使它们尽可能清晰!
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]]
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] 这个定义格式与 apply[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]chat[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]template 中使用的工具模式相同,唯一的区别是添加了 tool 装饰器:可以在我们的工具使用 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] 中[了解更多](https://huggingface.co/blog/unified-tool-use#passing-tools-to-a-chat-template).
然后,您可以直接初始化您的智能体:
```py
from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent
agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]download[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool], llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine=llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine)
agent.run(
"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]an you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ub?"
)
```
您将得到以下输出:
```text
======== [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ew task ========
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]an you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ub?
==== [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent is executing the code below:
most[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]downloaded[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]model = model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]download[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool(task="text-to-video")
print(f"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]downloaded[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]model}.")
====
```
输出:
`"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]he most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]yteDance/[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]nimateDiff-Lightning."`
### 管理智能体的工具箱
如果您已经初始化了一个智能体,但想添加一个新的工具,重新初始化智能体会很麻烦。借助 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ransformers,您可以通过添加或替换工具来管理智能体的工具箱。
让我们将 `model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]download[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool` 添加到一个仅初始化了默认工具箱的现有智能体中。
```python
from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent
agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[], llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine=llm[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]engine, add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue)
agent.toolbox.add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool(model[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]download[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool)
```
现在,我们可以同时使用新工具和之前的文本到语音工具:
```python
agent.run(
"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]an you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ugging [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ace [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ub and return the audio?"
)
```
| **[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]udio** |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| <audio controls[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]<source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] |
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] [W[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]]
[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>] 当向一个已经运行良好的代理添加工具时要小心,因为这可能会导致选择偏向你的工具,或者选择已经定义的工具之外的其他工具。
使用 agent.toolbox.update[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool() 方法可以替换智能体工具箱中的现有工具。
如果您的新工具完全替代了现有工具,这非常有用,因为智能体已经知道如何执行该特定任务。
只需确保新工具遵循与替换工具相同的 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>][YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>],或者调整系统提示模板,以确保所有使用替换工具的示例都得到更新。
### 使用工具集合
您可以通过使用 [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ollection 对象来利用工具集合,指定您想要使用的工具集合的 slug。
然后将这些工具作为列表传递给智能体进行初始化,并开始使用它们!
```py
from transformers import [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ollection, [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent
image[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]collection = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ollection(collection[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f")
agent = [YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]eact[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]ode[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]gent(tools=[*image[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tool[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]collection.tools], add[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]base[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]tools=[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]rue)
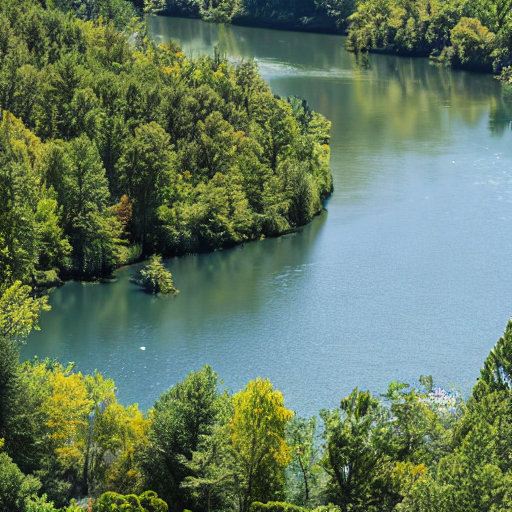
agent.run("[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]lease draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
```
为了加速启动,工具仅在智能体调用时加载。
这将生成如下图像:
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]and[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]lakes.png"[YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>]
[[在colab里打开]]
大型语言模型(LLM)经过 因果语言建模训练 可以应对各种任务,但在一些基本任务(如逻辑推理、计算和搜索)上常常表现不佳。当它们被用在自己不擅长的领域时,往往无法生成我们期望的答案。
为了解决这个问题,可以创建智能体.
智能体是一个系统,它使用 LLM 作为引擎,并且能够访问称为工具的功能。
这些工具是执行任务的函数,包含所有必要的描述信息,帮助智能体正确使用它们。
智能体可以被编程为:
CodeAgentReactJsonAgent此智能体包含一个规划步骤,然后生成 Python 代码一次性执行所有任务。它原生支持处理不同输入和输出类型,因此推荐用于多模态任务。
这是解决推理任务的首选代理,因为 ReAct 框架 (Yao et al., 2022) 使其在基于之前观察进行推理时非常高效。
我们实现了两种版本的 ReactJsonAgent:
ReactJsonAgentReactCodeAgent[TIP] 阅读 Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents 博文,了解更多关于推理智能体的信息。


以下是一个推理代码智能体如何处理以下问题的示例:
>>> agent.run( ... "How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?", ... ) =====New task===== How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need? ====Agent is executing the code below: bert_blocks = search(query="number of blocks in BERT base encoder") print("BERT blocks:", bert_blocks) ==== Print outputs: BERT blocks: twelve encoder blocks ====Agent is executing the code below: attention_layer = search(query="number of layers in Attention is All You Need") print("Attention layers:", attention_layer) ==== Print outputs: Attention layers: Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position- 2 Page 3 Figure 1: The Transformer - model architecture. ====Agent is executing the code below: bert_blocks = 12 attention_layers = 6 diff = bert_blocks - attention_layers print("Difference in blocks:", diff) final_answer(diff) ==== Print outputs: Difference in blocks: 6 Final answer: 6
要初始化一个智能体,您需要以下参数:
在智能体系统初始化时,工具属性将生成工具描述,并嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,告知智能体可以使用哪些工具,并且为什么使用它们。
安装依赖
首先,您需要安装智能体所需的额外依赖:
pip install transformers[agents]
创建LLM引擎
定义一个
llm_enginecallablestopfrom huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>") client = InferenceClient(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct") def llm_engine(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]) -> str: response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000) answer = response.choices[0].message.content return answer
您可以使用任何符合以下要求的
llm_engineList[Dict[str, str]]stop_sequences此外,
llm_enginegrammargrammarllm_engine您还需要一个
toolsToolsadd_base_tools=True现在,您可以创建一个智能体,例如 [
CodeAgentTransformersEnginetransformersLlama-3.1-70B-InstructHfApiEnginehuggingface_hub.InferenceClientfrom transformers import CodeAgent, HfApiEngine llm_engine = HfApiEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct") agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True) agent.run( "Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and return the audio.", sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?", )
当你急需某个东西时这将会很有用! 您甚至可以将
llm_engineHfApiEnginefrom transformers import CodeAgent agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True) agent.run( "Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and give me the audio.", sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?", )
请注意,我们使用了额外的
sentence您还可以使用这个来指定本地或远程文件的路径供模型使用:
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True) agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in New York?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
系统提示和输出解析器会自动定义,但您可以通过调用智能体的
system_prompt_templateprint(agent.system_prompt_template)
尽可能清楚地解释您要执行的任务非常重要。 每次 [
~Agent.runagent.taskagent.logsPython 解释器在一组输入和工具上执行代码。 这应该是安全的,因为只能调用您提供的工具(特别是 Hugging Face 的工具)和 print 函数,因此您已经限制了可以执行的操作。
Python 解释器默认不允许导入不在安全列表中的模块,因此大多数明显的攻击问题应该不成问题。 您仍然可以通过在 [
ReactCodeAgentCodeAgentadditional_authorized_imports>>> from transformers import ReactCodeAgent >>> agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4']) >>> agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?") (...) 'Hugging Face – Blog'
如果有任何代码尝试执行非法操作,或者生成的代码出现常规 Python 错误,执行将停止。
[!WARNING] 在使用大语言模型(LLM)生成代码时,生成的代码会被执行,避免导入或使用任何不安全的库或模块。
智能体,或者说驱动智能体的 LLM,根据系统提示生成输出。系统提示可以定制并根据目标任务进行调整。例如,检查 [
ReactCodeAgentYou will be given a task to solve as best you can. You have access to the following tools: <<tool_descriptions>> To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences. At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use. Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence. During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need. These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step. In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool. Here are a few examples using notional tools: --- {examples} Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have acces to those tools: <<tool_names>> You also can perform computations in the python code you generate. Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward. Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks. Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result. Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined. Now Begin!
系统提示包括:
<<tool_descriptions>>namedescriptioninputsoutput_typejinja2您可以通过向
system_promptfrom transformers import ReactJsonAgent from transformers.agents import PythonInterpreterTool agent = ReactJsonAgent(tools=[PythonInterpreterTool()], system_prompt="{your_custom_prompt}")
[WARNING] 必须在
中定义template这个变量,以便智能体能够正确地识别并使用可用的工具<<tool_descriptions>>
以下是检查运行后发生了什么的一些有用属性:
agent.logsagent.logsagent.write_inner_memory_from_logs()工具是智能体使用的基本功能。
例如,您可以检查 [
PythonInterpreterTool__call__当智能体初始化时,工具属性会用来生成工具描述,然后将其嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,这让智能体知道可以使用哪些工具以及为什么使用它们。
Transformers 提供了一个默认工具箱,用于增强智能体,您可以在初始化时通过
add_base_tools=TrueDuckDuckGoReactJsonAgentadd_base_tools=True您可以通过调用 [
load_toolfrom transformers import load_tool tool = load_tool("text-to-speech") audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
您可以为
Hugging FaceHugging Face Hub您将从以下代码开始:
from huggingface_hub import list_models task = "text-classification" model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1))) print(model.id)
这段代码可以很快转换为工具,只需将其包装成一个函数,并添加
toolfrom transformers import tool @tool def model_download_tool(task: str) -> str: """ This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. It returns the name of the checkpoint. Args: task: The task for which """ model = next(iter(list_models(filter="text-classification", sort="downloads", direction=-1))) return model.id
该函数需要:
model_download_toolArgs所有这些将自动嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,因此请尽量使它们尽可能清晰!
[TIP] 这个定义格式与 apply_chat_template 中使用的工具模式相同,唯一的区别是添加了 tool 装饰器:可以在我们的工具使用 API 中了解更多.
然后,您可以直接初始化您的智能体:
from transformers import CodeAgent agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine) agent.run( "Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?" )
您将得到以下输出:
======== New task ======== Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub? ==== Agent is executing the code below: most_downloaded_model = model_download_tool(task="text-to-video") print(f"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most_downloaded_model}.") ====
输出:
"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning."如果您已经初始化了一个智能体,但想添加一个新的工具,重新初始化智能体会很麻烦。借助 Transformers,您可以通过添加或替换工具来管理智能体的工具箱。
让我们将
model_download_toolfrom transformers import CodeAgent agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True) agent.toolbox.add_tool(model_download_tool)
现在,我们可以同时使用新工具和之前的文本到语音工具:
agent.run( "Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub and return the audio?" )
| Audio |
|---|
[WARNING] 当向一个已经运行良好的代理添加工具时要小心,因为这可能会导致选择偏向你的工具,或者选择已经定义的工具之外的其他工具。
使用 agent.toolbox.update_tool() 方法可以替换智能体工具箱中的现有工具。 如果您的新工具完全替代了现有工具,这非常有用,因为智能体已经知道如何执行该特定任务。 只需确保新工具遵循与替换工具相同的 API,或者调整系统提示模板,以确保所有使用替换工具的示例都得到更新。
您可以通过使用 ToolCollection 对象来利用工具集合,指定您想要使用的工具集合的 slug。 然后将这些工具作为列表传递给智能体进行初始化,并开始使用它们!
from transformers import ToolCollection, ReactCodeAgent image_tool_collection = ToolCollection(collection_slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f") agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection.tools], add_base_tools=True) agent.run("Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
为了加速启动,工具仅在智能体调用时加载。
这将生成如下图像:
